Thermodynamic derivation of the Stefan-Boltzmann Law
In this article the Stefan-Boltzmann-Law is to be derived using the laws of thermodynamics.
Introduction
In this article, the Stefan-Boltzmann Law is to be derived with...
Different forms of Planck’s law
Planck's law of radiation can be expressed in different forms. The most important ones are discussed in this article.
Introduction
Planck's law of radiation describes the...
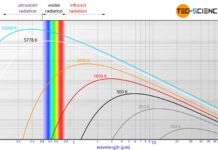
Planck’s law and Wien’s displacement law
Planck's law describes the radiation emitted by black bodies and Wien's displacement law the maximum of the spectral intensity of this radiation.
Blackbody radiation
The emitted...
Stefan-Boltzmann law & Kirchhoff’s law of thermal radiation
The Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the radiant power of an object in thermal equilibrium is proportional to the fourth power of temperature and directly...
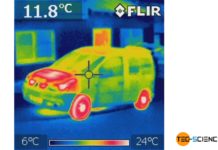
How does a thermal imaging camera work?
Thermal imaging cameras are based on the same principle as the pyrometer. These cameras capture the radiation spectrum of an object, which then allows...
How does a infrared thermometer (pyrometer) work?
Pyrometers (infrared thermometers) use the heat radiation of objects invisible to the human eye to determine the temperature!
The thermometers presented in the previous articles...
How does a thermocouple work?
In this article we will deal with the design and operation of a thermocouple which is used to measure temperatures.
Seebeck effect
A thermocouple uses the...
How does a resistance temperature detector (resistance thermometer) work?
In resistance thermometers the dependence of the electrical resistance on the temperature is used to determine the temperature!
Operating principle
A further measuring principle for determining...
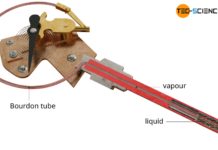
How does a vapor pressure thermometer (vapor-in-metal) work?
Vapor pressure thermometers use the temperature-dependent vapor pressure of a liquid as the measuring principle.
The less popular vapour pressure thermometers work according to the...
How does a gas filled thermometer (gas-in-metal) work?
In gas thermometers, the pressure rise connected with a temperature increase is used for measuring the temperature!
In gas filled temperature gauges (also called gas...
How does a liquid filled thermometer (liquid-in-metal) work?
Liquid-in-metal thermometers use the pressure rise of a liquid that comes along with an increase in temperature, if the volume is kept constant!
In liquid-in-metal...
How does a bimetallic strip thermometer work?
In bimetallic strip thermometers the different rates of expansion of metals when heated is used to measure the temperature!
Operating principle
Temperatures can be meassured based...
How does a liquid-in-glass thermometer work?
In liquid-in-glass thermometers, the thermal expansion of liquids is used for measuring the temperature!
Operating principle
Liquid-in-glass thermometers are based on the principle of thermal expansion...
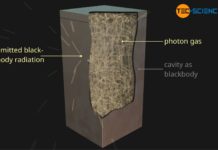
Blackbody radiation
Blackbody radiation (cavity radiation) is the thermal radiation of a blackbody, i.e. a body that absorbs all incident radiation.
Blackbody
When white light hits an opaque...
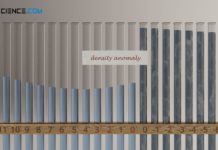
Density anomaly of water (negative thermal expansion)
Density anomaly refers to the paradoxical behavior of a substance to expand suddenly when cooling down instead of contracting further (anomalous decrease in density).
Negative...
Temperature scales
Learn more about the origin of the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin temperature scales in this article.
Introduction
In everyday life, temperature is often understood as a...
Temperature and particle motion
The higher the temperature of a substance, the greater the kinetic energy of the particles!
Temperature
If matter is heated and thus its temperature rises more...
Particle model of matter
The particle model imagines matter made up of individual particles (atoms, molecules)!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KBmhSd7wb5Y
The particle model of matter
The central model for the description of thermodynamic processes...