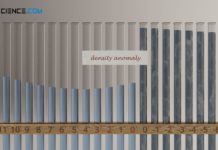
Density anomaly of water (negative thermal expansion)
Density anomaly refers to the paradoxical behavior of a substance to expand suddenly when cooling down instead of contracting further (anomalous decrease in density).
Negative thermal expansion (density anomaly)
Due to its special...
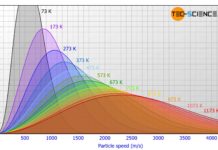
Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution
The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes the distribution of the molecular speed of the molecules in ideal gases.
Introduction
As already explained in the article Temperature and particle motion, the temperature of a gas is...
Why do liquids evaporate?
In this article, learn how the evaporation of liquids can be qualitatively explained using the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of ideal gases
The figure below shows the speed distribution according to Maxwell-Boltzmann for...
Temperature scales
Learn more about the origin of the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin temperature scales in this article.
Introduction
In everyday life, temperature is often understood as a quantity that expresses the property of a...
Why does metal feel colder than wood (human thermal response)?
Find out in this article why metal feels colder than wood of the same temperature, while at higher temperatures the metal suddenly feels warmer than wood.
The property of an object to...
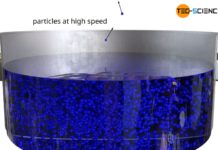
Temperature and particle motion
The higher the temperature of a substance, the greater the kinetic energy of the particles!
Temperature
If matter is heated and thus its temperature rises more and more, it can be seen that...
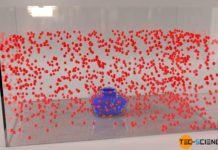
Particle model of matter
The particle model imagines matter made up of individual particles (atoms, molecules)!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KBmhSd7wb5Y
The particle model of matter
The central model for the description of thermodynamic processes is the particle model, which will be...