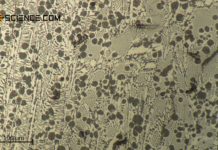
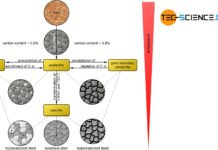
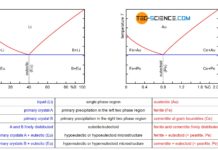
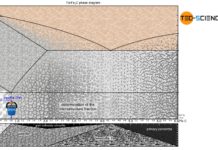
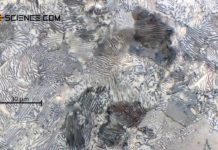
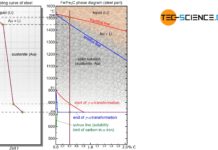
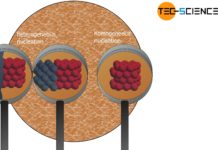
Solution annealing of steel
The aim of solution annealing is to dissolve formed precipitates!
During welding or hot forming, microstructural changes occur in the steel due to the influence...
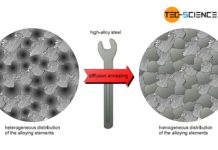
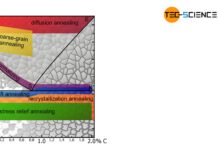
Diffusion annealing of steel
The aim of diffusion annealing is to compensate for concentration differences!
When steels with high alloy concentrations solidify, the alloying elements may not be distributed...
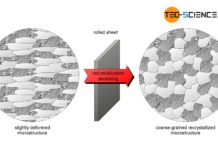
Recrystallization annealing of steel
The aim of recrystallisation annealing is to restore a deformed microstructure to improve its deformability!
The microstructure of rolled, bent or deep-drawn workpieces is strongly...
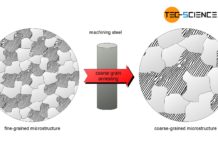
Coarse-grain annealing of steel
The aim of coarse grain annealing is to improve machinability!
In general a coarse-grained steel microstructure is undesirable due to the relatively low toughness and...
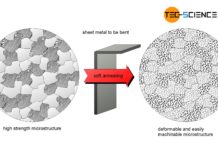
Soft annealing of steel
The aim of soft annealing is to improve formability and machinability!
Not every material has to be designed to withstand high mechanical forces. With a...
Nitriding of steel (surface hardening)
Nitriding is not based on the formation of martensite but on the formation of hard and wear-resistant nitrides on the surface of the workpiece!
Surface...
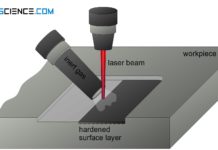
Laser hardening of steel (surface hardening)
With laser hardening, the surface is heated by a laser beam and quenched by heat dissipation in the workpiece (self quenching)!
Laser-beam hardening (laser hardening)...
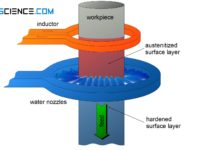
Induction hardening of steel (surface hardening)
With induction hardening, the workpiece is heated by induced eddy currents. The hardening depth is controlled by the frequency of the alternating current!
The flames...
Flame hardening of steel (surface hardening)
Surface hardening is used to produce a hard and wear-resistant surface layer on steel workpieces, while the toughness in the core is largely retained.
Introduction
A...
Eddy current testing (ECT)
Eddy current testing is used to non-destructively inspect components for surface defects such as cracks.
With eddy current testing, electrically conductive materials can be examined...
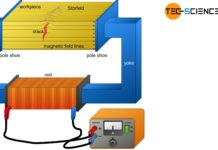
Magnetic particle inspection (MPI)
With magnetic particle inspection (MPI), surface defects such as cracks of ferromagnetic components are made visible.
Introduction
Like the dye penetrant inspection, magnetic particle inspection is...
Dye penetrant inspection (DPI)
With Dye penetrant inspection, cracks on the surface of components can be made visible in a non-destructive manner.
The dye penetrant inspection (or liquid penetrate...
Ultrasonic testing (UT)
Ultrasonic testing uses sound waves to non-destructively inspect a component for flaws.
Introduction
Ultrasonic testing is a non-destructive testing technique because the workpieces or components to...
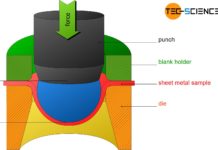
Cupping test
In the cupping test according to Erichsen, the deep drawing behavior of a metal sheet is examined.
Sheets for deep-drawing applications must have very good...
Stress-relaxation test
The relaxation strength indicates for a certain temperature to which value the stress falls at a given strain after a certain time!
In the creep...
Stress rupture test (creep rupture test)
The creep rupture test (stress rupture test) is used to measure the strength of materials that are subjected to constant stress at elevated temperatures.
Creep
If...
Fatigue test
The fatigue test provides information about the strength of a material under continuously changing stress (dynamic load).
Introduction
The intensity of the stress increases slowly but...
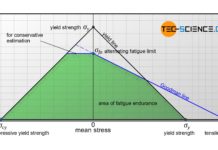
Fatigue limit diagram according to Haigh and Smith
Fatigue limit diagrams according to Haigh or Smith show the maximum yieldable stress amplitude as a function of the mean stress.
Fatigue limit diagrams
Although the...
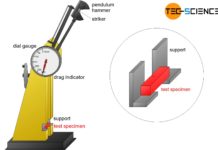
Charpy impact test
The Charpy impact test (Charpy V-notch test) is used to measure the toughness of materials under impact load at different temperatures!
Introduction
The elongation at break...
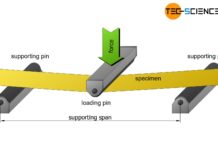
Bending flexural test
In a bending flexural test, a standardized specimen is bent under uniaxial bending stress until plastic deformation or fracture occurs!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B-caaAtTsDk
Test setup
In the bending flexural...
Compression test
In the compression test, a standardized specimen is loaded under compressive stress until it breaks or until a first crack appears.
The testing of materials...
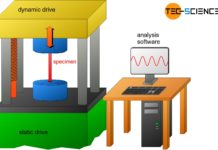
Tensile test
The tensile test is used to determine the strength (yield point, ultimate tensile strength) and toughness (elongation at break) of a material!
Setup
The tensile test...
Destructive material testing & non-destructive testing (NDT)
In destructive materials testing, the material is damaged; in non-destructive materials testing, the workpiece is left undamaged.
Materials such as steels generally have to withstand...
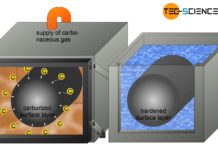
Case hardening (surface hardening)
With case hardening, low-carbon steels are first enriched with carbon in the surface layer (carburisation) and then quenched!
Case hardening
The toughness (ductility) of steels increases...
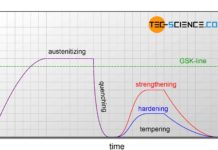
Quenching and tempering of steel
The aim of quenching and tempering is to achieve a hard and wear-resistant surface or to increase the strength of a workpiece.
Introduction
The heat treatments...
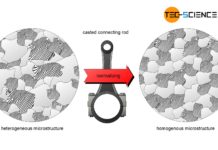
Normalizing of steel (annealing)
The aim of normalizing is to achieve a uniform homogeneous microstructure with reproducible properties!
As already explained in the chapter deformability of metals, fine roundish...
Overview of heat treatment of steel
Heat treatment processes are used to specifically influence the properties of the steel.
The microstructure of a steel has a particular influence on its properties....
Cast iron
https://youtu.be/lSfmU8cmzLE
Introduction
Up to now, the iron-carbon phase diagram has only been considered up to a carbon content of 2.06 %. If this carbon content is...
Summary of the phase transformations of steel
In this article, a summary is given about the phase transformations during solidification and cooling of steel.
https://youtu.be/b581J_SmCM4
Introduction
In the article Phase transformations in the solidified...
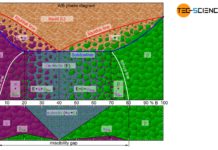
Comparison of phase transformations in steels
Phase transformations in steels can be compared to those of solid solutions (completely soluble) and crystal mixtures (completely insoluble).
https://youtu.be/b581J_SmCM4
The figure below shows steel part...
Determination of microstructure and phase fractions in steels
For steels, the microstructure and phase fractions in the iron-carbon diagram can be determined using the lever rule.
https://youtu.be/b581J_SmCM4
Introduction
For many applications it is important to...
Influence of carbon on hardness and strength of steels
With increasing carbon, the hardness and strength of unalloyed steels increases. Above a content of 0.8% C, the strength decreases.
As the carbon content increases,...
Phase transformations of steels in solidified state (metastable system)
Depending on the carbon content, further phase transformations take place in the steel in the solidified state. The cooled microstructure consists of pearlite and...
Microstructure formation of steels during solidification
Steels solidify as solid solutions. The face-centered cubic lattice structure with the embedded carbon atom is called austenite.
https://youtu.be/b581J_SmCM4
Introduction
In principle, steels are binary systems consisting...
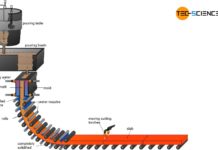
From steel to semi-finished products
Semi-finished products are mainly produced by (discontinuous) ingot casting or by continuous casting.
Ingot casting
With ingot casting, the molten steel from the steelworks solidifies in...
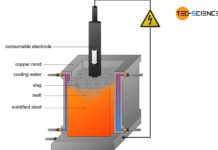
From crude steel to steel
In order to meet today's requirements for steels, crude steel must be further treated by various processes after it has been refined.
Introduction
In the early...
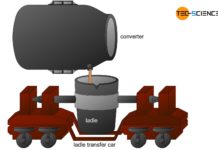
From pig iron to crude steel
After the pig iron has been tapped, it must be desulfurized and oxidized with oxygen (refining) to obtain crude steel.
Introduction
Due to its high carbon...
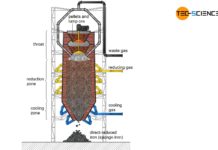
Direct reduced iron process
The direct reduced iron process (DRI) is becoming more and more important in the climate change debate about producing steel with as little CO2...
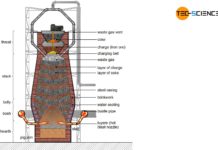
Blast furnace process
In the blast furnace, the iron ore reacts with the carbon contained in the coke to form grey or white pig iron.
Combustion process
The iron...
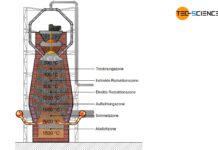
Ironworks
Steel is produced from iron ore in the ironworks. The ironworks includes charging, coking plant, Cowper stove and the blast furnace.
Charging
After the ground ores...
Iron ore mining and dressing
After the iron ore has been mined, it has to be processed for use in the blast furnace in order to optimize the chemical...
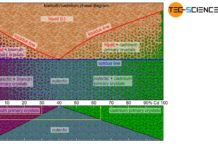
Alloys – limited solubility of components in solid state
In general, the components of alloys are soluble in each other only to a limited extent. In this case, a mixture of solid solutions...
Alloys – complete insolubility of components in solid state
If the components of an alloy are completely insoluble in each other in the solid state, then a mixture of pure crystals is formed.
https://youtu.be/6NFBEoPMMv0
Introduction
If...
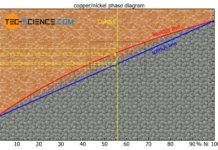
Alloys – complete solubility of components in solid state (solid solution)
If the components of an alloy are completely soluble in each other in the solid state, then solid solutions form.
https://youtu.be/N-RQntCjTZk
Introduction
If the two components of...
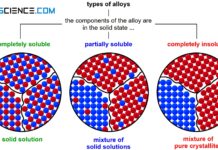
Typs of alloys
Depending on the extent to which the two components are soluble in each other in the solid state, different types of alloys result.
https://youtu.be/Ig7UV8yTlOs
Introduction
In many...
Types of nuclei
Solidification can be triggered either by nuclei consisting of the same substance as the melt or by nuclei consisting of a different substance.
https://youtu.be/7xPfW2hYt8w
Introduction
As explained...
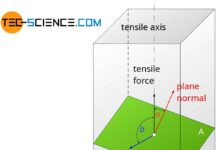
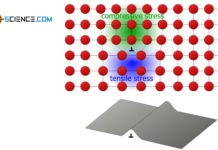
Schmid’s law
External normal stresses induce shear stresses inside a material, which become maximum at an angle of 45°.
https://youtu.be/AaHxsDl2ZWg
Shear force
If a material is stressed under tension,...
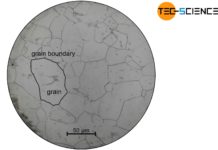
Microstructure formation
The solidification of a melt starts from nuclei, resulting in the typical polycrystal microstructure.
https://youtu.be/7xPfW2hYt8w
Polycrystal
A metallic material generally does not have a uniform lattice orientation...
Crystal growth
In polygonal crystal growth, the heat of solidification is transferred through the crystal and in dendritic crystal growth through the melt.
https://youtu.be/LOmCxNNbDN4
Introduction
In the article homogeneous...
Heterogeneous nucleation
In heterogeneous nucleation, nuclei that do not consist of the same substance as the melt trigger solidification.
https://youtu.be/CtKK6Vznd4Y
Introduction
The nucleation considered in the article homogeneous nucleation...
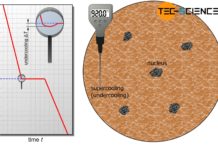
Homogeneous nucleation
In homogeneous nucleation, nuclei consisting of the same substance as the melt trigger solidification.
https://youtu.be/uyYxyTKEIzg
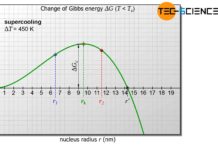
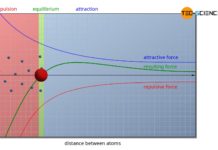
Gibbs energy
In order to understand the processes of nucleation, an energetic...
Amorphous metals
In amorphous metals, supercooling is so strong that nucleation is suppressed and crystalline structures do not form.
In the article on types of nuclei it was...
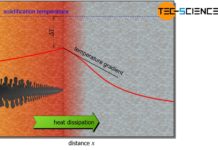
Heat of solidification
During solidification, heat is released, which is called heat of crystallization or heat of solidification. It counteracts the external cooling.
https://youtu.be/7xPfW2hYt8w
Introduction
The hand warmer described in...
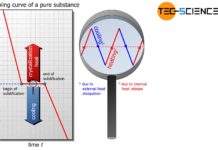
Conditions for solidification
Two conditions must be met for solidification: The melt must be supercooled and nuclei must be present in the melt.
https://youtu.be/7xPfW2hYt8w
Introduction
The origin for the...
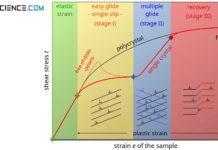
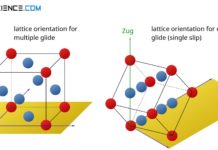
Deformation process in single crystals
Deformation in single crystals is divided into four stages: elastic, easy glide (single slip), multiple glide and recovery.
https://youtu.be/meUF-9i-4Qw
Introduction
Even if single crystals are used far less than polycrystals,...
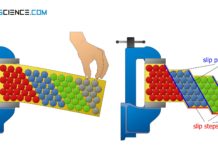
Deformation of ideal crystal structures (single crystal)
During the deformation of single crystals, slip steps preferably form at 45° to the tensile axis, since the shear stresses are at a maximum.
https://youtu.be/xaNPAMxLXdE
Introduction
If...
Deformation process in real crystal structures
Dislocations provide low-stress deformation due to the gradual sliding of atomic blocks.
https://youtu.be/54H5HQlMEio
Introduction
To initiate a deformation process, a certain critical resolved shear stress (CRSS) is...
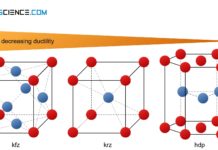
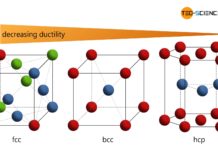
Influence of the lattice structure on ductility
Each type of lattice structure has a different number of slip systems (possibilities of sliding) and is therefore differently deformable.
Slip system
As explained in the article on Fundamentals...
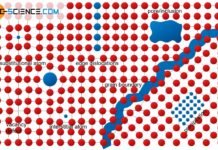
Crystallographic defects
Crystallographic defects are deviations from an ideal microscopic lattice structure of metals such as vacancies or dislocations.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EoCtPYHaRAE
Introduction
The previous article dealt with a uniform and...
Derivation of the packing density
The packing density is the ratio of the atomic volume within a unit cell to the volume of the unit cell.
https://youtu.be/gjdb9QfRg0I
Definition of the packing...
Fundamentals of deformation
Deformation of metals is based on the shifting or sliding of atomic blocks. A distinction is made between elastic and plastic deformation.
Introduction
The relatively good...
Important types of lattice structures
Important lattice structures are the face-centered cubic (fcc), the body-centered cubic (bcc), and the hexagonal closest packed (hcp).
Introduction
The article on lattice structure of metals...
Lattice structure of metals
The lattice structure is the periodic structure of metals. The lattice structure is characterized by the unit cell.
Introduction
Metals play an important role in mechanical...